Monocrotaline induced Pulmonary Hypertension (PAH)
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is one form of a broader condition known as pulmonary hypertension, which is high blood pressure in the lungs.
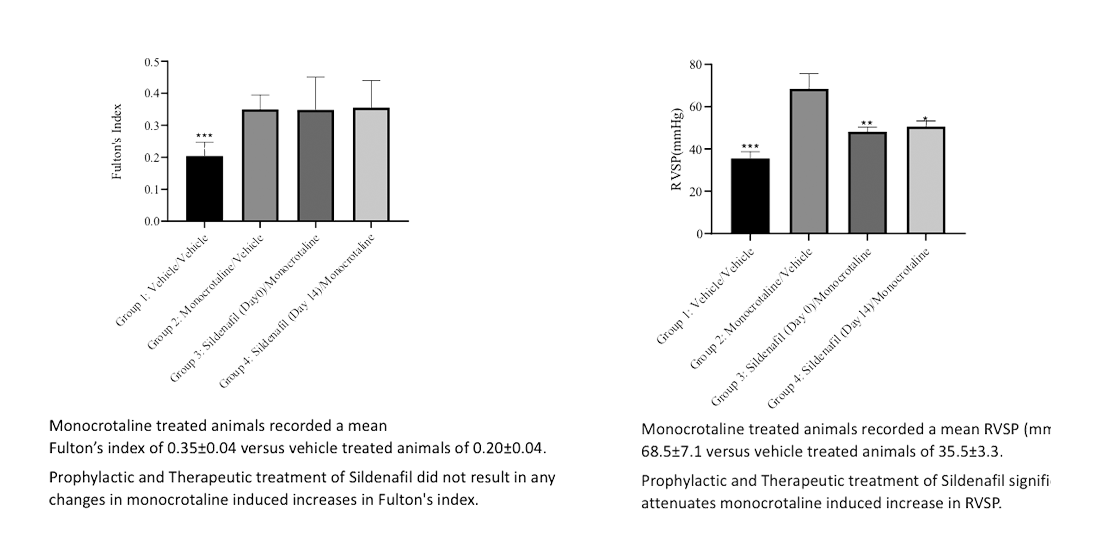
In rats, a single subcutaneous administration of monocrotaline induces increases in right ventricular (RV) pressure and pulmonary vascular modelling, approximately 4 weeks after monocrotaline administration.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | SD rat |
| Model | Monocrotaline induced pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) rat model |
| Relevant Use | Assessing the efficacy of new compounds for PAH |
| Readouts Available | Bodyweights and Clinical Signs, invasive hemodynamic measurements (RVSP), Fulton’s index, histopathology (H&E, van Gieson) |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery -
Flu Model: H1N1 influenza lung infection model – viral COPD exacerbation
Discovery -
Model of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Mice
Discovery
