Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Chlorine Gas Injury can lead to epithelial injury, airway remodelling and potentially ARDS. Inhalation models of chlorine toxicity provide unique opportunities for testing potential pharmacologic rescue agents.
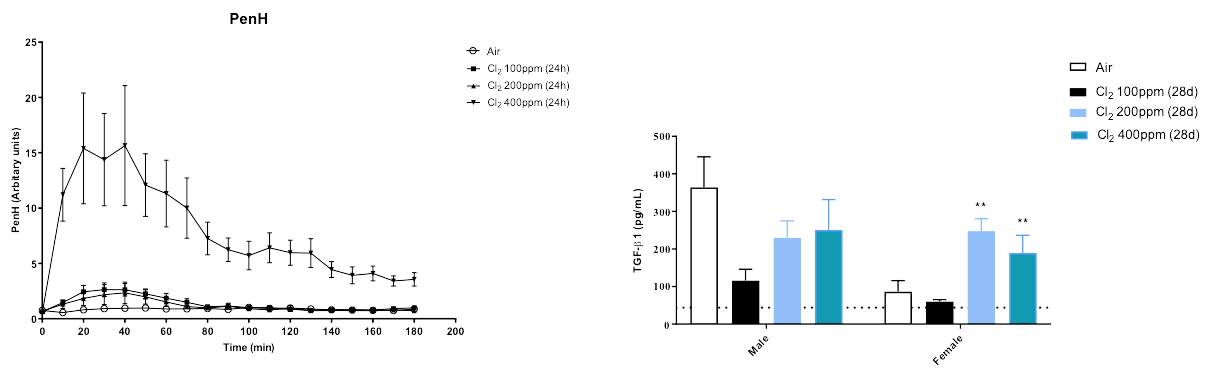
Labcorp’s chlorine exposure model has demonstrated significant increases in tidal volume, penh and lower respiratory rates, lung odema, increases in BAL IL-1β, MIP-1α, MCP-1 and clinical signs.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | SD rat |
| Model | Chlorine Induced Lung Injury |
| Relevant Use | Assessing the efficacy of novel compounds targeted at chemical lung injury |
| Readouts Available | Clinical signs, bodyweight, Lung function (WBP and invasive), lung oedema, BAL differential cell counts, and BAL cytokines, histopathology |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery -
Flu Model: H1N1 influenza lung infection model – viral COPD exacerbation
Discovery -
Model of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Mice
Discovery
