COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Neutrophil Elastase plays an important role in the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), resulting in extensive tissue damage and malfunctioning of the airways.
Administration of human neutrophil elastase induces haemorrhage in the lungs which is measured by an increase in haemoglobin and red blood cells in the BAL.
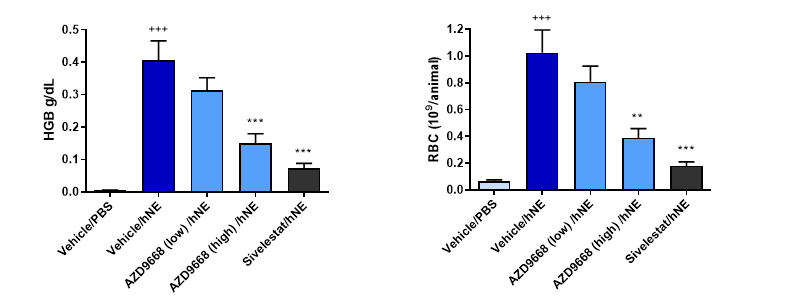
Administration of human neutrophil elastase induces haemorrhage, this is reversed by administration of the positive control Sivelestat (human NE inhibitor) and AZD9668.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | SD rat |
| Model | Human neutrophil elastase |
| Relevant Use | Assessing the efficacy of novel compounds targeted at neutrophil elastase |
| Readouts Available | BAL Haemoglobin levels, BAL differential cell counts, and BAL cytokines |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery -
Flu Model: H1N1 influenza lung infection model – viral COPD exacerbation
Discovery -
Model of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Mice
Discovery
