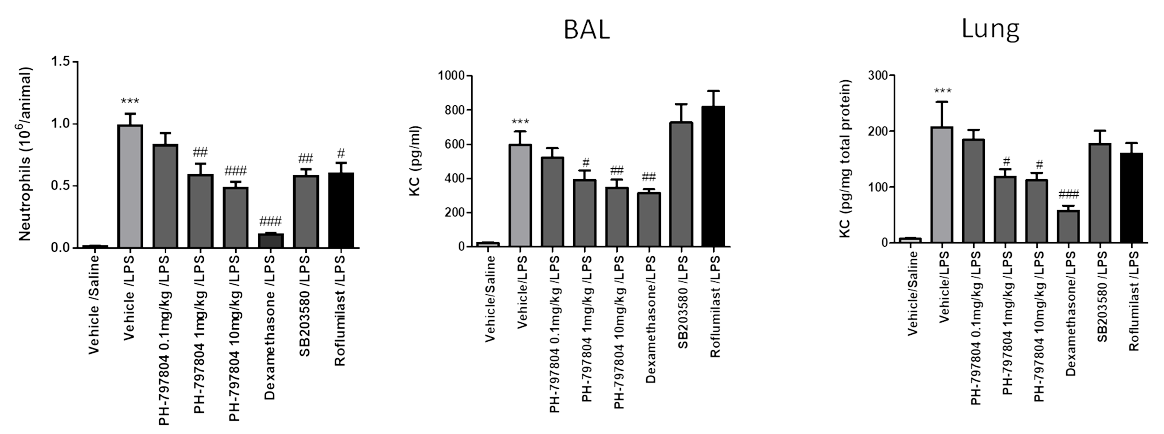
COPD: LPS neutrophil chemotaxis model (inhaled)
A key hallmark of COPD is airway neutrophilia – administration of LPS induces neutrophil chemotaxis to the lungs.
In the short (1 day) acute model of inflammation, LPS can be administered as either a nebulized aerosol or via the intratracheal route.
Validated positive controls – budesonide, dexamethasone, roflumilast and fluticasone propionate.
| Study Design | |
|---|---|
| Species/Strain | SD rat, Balb/c mouse, C57BL/6J mouse, guinea pig |
| Model | LPS induced Neutrophil Chemotaxis |
| Relevant Use | Assessing novel anti-inflammatories |
| Readouts Available | BAL differential cell counts and BAL cytokines |
Study data generated by Labcorp Huntingdon Pharmacology.
Related Models
-
Bhas 42 Cell Transformation Assay (CTA)
Carcinogenicity, Discovery, Toxicology -
Asthma: Ovalbumin sensitization and challenge
Discovery -
Chlorine Induced Lung Injury
Discovery -
COPD: LPS + fMLP PK/PD model – Neutrophil Elastase Targets
Discovery -
COPD: Human Neutrophil Elastase Lung Hemorrhage Model
Discovery -
Bronchoconstriction models for LABA, LAMA & MABAs
Discovery -
Flu Model: H1N1 influenza lung infection model – viral COPD exacerbation
Discovery -
Model of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Mice
Discovery
